The Ketogenic Diet: A Game Changer for Mental Health
Developed to treat epilepsy in children, the Keto diet is now successfully alleviating symptoms of a growing number of mental health disorders, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, seizure disorders and obesity. Emerging research believes it may be a possible solution to Alzheimers disease

The ketogenic diet, a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan, has recently gained significant popularity. While initially developed as a treatment for epilepsy, it is being used widely for its benefits in mental health. Pioneering nutritional psychiatrists and scientists have been at the forefront of studying the ketogenic diet's impact on a wide range of serious mental health conditions, suggesting it could be a revolutionary approach to treatment.
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet typically has a macronutrient ratio of about 70-80% fat, 15-20% protein, and only 5-10% carbohydrates. This drastic reduction in carbohydrates puts the body into a metabolic state called ketosis, which uses fat and ketones for fuel instead of glucose.
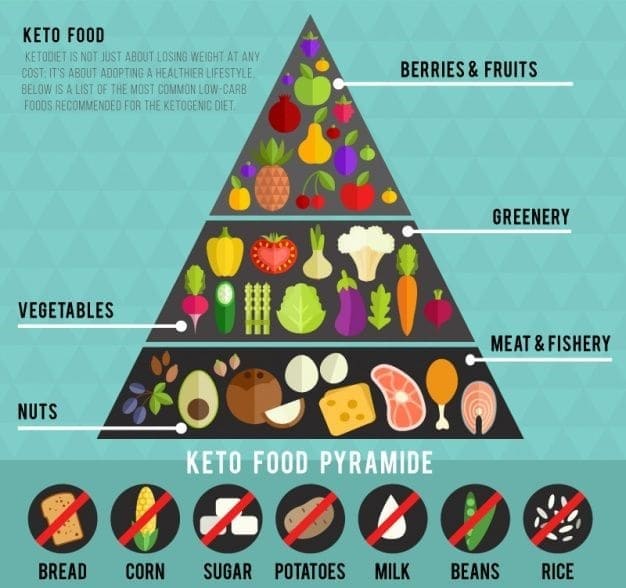
Originally developed in the 1920s to treat epilepsy in children, the ketogenic diet is now being recommended for its potential and ability to alleviate symptoms of various mental health disorders.
What are Keytones?
When your carbohydrate intake is low and your protein intake is just right, your blood sugar and insulin will gradually fall to lower, healthier levels and become more stable. Under these conditions, your body will start to break down fat and transform it into ketones that many cells can burn for energy instead of glucose (sugar). These ketones are released into the bloodstream and can be measured at home using a blood ketone meter. There are three types of ketones, but the one that our cells prefer to use is called beta-hydroxybutyrate:
- acetone can't be burned by cells for energy and comes out in your breath. This is the ketone measured by breath analyzers. Once fully adapted to a ketogenic diet (which can take at least 3 weeks) muscle cells can turn acetone into beta-hydroxybutyrate.
- acetoacetate is the ketone measured by urine ketone strips. Its metabolism is complicated. Urine acetoacetate levels may fall as you adapt to a ketogenic diet, so urine strips sometimes aren't as reliable over the long term. Acetoacetate can break down into either acetone or beta-hydroxybutyrate.
- beta-hydroxybutyrate is the most efficient fuel source for cells, and the primary ketone found in the blood when in ketosis. This is the ketone measured by blood ketone strips.
Ideal blood ketone recommendations vary widely among experts, but generally speaking, if your blood ketone level falls between 0.5 mM and 5.0 mM, you are "in ketosis." Some clinicians recommend aiming for the higher end of this range if you are trying to treat a serious medical condition such as cancer, epilepsy, or schizophrenia. However, people trying to lose excess body fat, normalize diabetic blood glucose levels, or treat other simpler conditions, find it sufficient to generate ketones between approximately 1.0 and 2.5 mM.
The Gut-Brain Connection
Recent research has highlighted the profound effects of the ketogenic diet on the gut microbiome. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication system between the gastrointestinal and central nervous systems, plays a crucial role in mental health. The ketogenic diet may indirectly influence brain function and mental well-being.
Studies have shown that individuals with certain mental health conditions often have altered gut microbiomes. The ketogenic diet's ability to optimize gut function could be one of the mechanisms by which it improves mental health outcomes.
Diet's Impact On The Gut Microbiome Involves Multiple Mechanisms
- Alternative brain fuel: Ketones provide an efficient energy source for the brain, potentially improving cognitive function and mood stability. Enhanced mitochondrial function: - The diet may boost mitochondrial efficiency and improve energy metabolism in brain cells. - Neurotransmitter regulation: Ketosis has been shown to influence the production and regulation of important neurotransmitters like GABA and glutamate - Reduced oxidative stress: The ketogenic diet has anti-inflammatory effects, reducing oxidative stress in the brain.
Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
There are many good reasons to change to a ketogenic diet. Burning fat is cleaner, safer, and more efficient for most cells than burning sugar (glucose).
"The more fat one burns as fuel, the healthier the person will be, and the more likely they will live a long time. The more sugar a person burns, the more disease-ridden and the shorter the lifespan a person is likely to have." - Dr R. Rosedale
Scientific research has revealed strong evidence that ketogenic diets can be useful in managing a wide variety of difficult-to-treat medical conditions, including the following:
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Epilepsy (seizure disorders)
- Heart disease
There is emerging evidence that ketogenic diets can be useful in managing the following:
There is emerging evidence that ketogenic diets can be useful in managing the following:
- Acne
- Alcoholism
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Amyotrophic lateral scoliosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease)
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Autism
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Depression and anxiety
- Headaches and migraines
- Multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson's Disease
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Sleep disorders
- Traumatic brain injury
Improved Mood and Reduced Stress
Several studies have reported improvements in mood and stress levels among individuals following a ketogenic diet. A large-scale survey conducted in 2023 found that participants reported increased calmness, contentedness, and alertness after adopting the diet. These effects may be due to the diet's ability to regulate neurotransmitters and reduce oxidative stress in the brain.

Benefits for Severe Mental Illness
A small but promising pilot study published in 2022 investigated the effects of the ketogenic diet on patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. The results were encouraging, with participants experiencing significant symptom improvements. Patients not only lost weight and improved metabolic markers but also reported better energy levels, sleep quality, mood, and overall quality of life. On average, there was a 31% improvement on the psychiatrist rating scale used to assess symptom severity.
Safety and Practical Considerations
While the ketogenic diet is generally considered safe for most individuals, it is important to note that it can increase LDL cholesterol levels in some people. However, the overall cardiovascular risk profile often improves due to weight loss and other metabolic benefits associated with the diet.
For those considering the ketogenic diet as a mental health intervention, working with your doctor and a qualified ketogenic dietitian is highly recommended. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure nutritional adequacy while monitoring potential side effects and drug interactions.

Key Take Aways
The ketogenic diet shows great promise in the treatment of a wide range of mental health conditions. While more research is needed on some psychiatric conditions, early evidence is encouraging and being implemented by many individuals and medical professionals globally.






