Parasites Unmasked: The Silent Invaders Threatening Global Health
Approximately 3.5 billion people worldwide are affected by parasitic infections annually. Over 1 billion people suffer from soil-transmitted helminth infections. Malaria, a parasitic disease, still causes over 619,000 deaths globally each year.

Parasitic infections represent one of the most pervasive yet often overlooked health challenges facing humanity today. Despite significant advances in medical science, these microscopic invaders pose significant global health challenges as they continue to impact millions of lives, causing a wide range of health complications that can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
The Scale of Parasitic Infections
Contrary to popular belief, parasitic infections are not confined to developing countries. Recent global health data reveals:
SHOCKING STATISTICS:
Approximately 3.5 billion people worldwide are affected by parasitic infections annually. Over 1 billion people suffer from soil-transmitted helminth infections. Malaria, a parasitic disease, still causes over 619,000 deaths globally each year.
Common Parasitic Infections
Some of the most common parasitic infections include:
- Trichomoniasis: A sexually transmitted infection caused by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis.
- Giardiasis: Caused by Giardia intestinalis, this infection leads to diarrhoea and abdominal pain.
- Cryptosporidiosis: This infection, caused by Cryptosporidium, results in watery diarrhoea and is often spread through contaminated water.
- Toxoplasmosis: Caused by Toxoplasma gondii, this infection can affect the brain and eyes, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Transmission Pathways: How Parasites Enter the Human Body
Invisible Routes of Infection
Parasites employ multiple transmission strategies, making prevention challenging:
- Contaminated Water Sources
- Drinking or contact with untreated water
- Poor sanitation infrastructure
- Agricultural and industrial water pollution

- Food-Borne Transmission
- Undercooked meats
- Unwashed fruits and vegetables
- Cross-contamination during food preparation
- Skin and Environmental Contact
- Walking barefoot in contaminated soil
- Swimming in infected water bodies
- Contact with infected animals or animal waste
Health Impacts: The Multifaceted Consequences of Parasitic Infections
Physical Health Complications: Parasitic infections can trigger a complex array of health issues:
- Digestive System Disruptions:
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Malabsorption of nutrients
- Intestinal inflammation
- Potential development of irritable bowel syndrome
- Immune System Challenges
- Weakened immune response
- Increased susceptibility to secondary infections
- Chronic inflammation
- Potential autoimmune complications
- Systemic Health Consequences
- Anemia
- Malnutrition
- Organ damage
- Neurological complications
- Developmental delays in children
- Psychological and Economic Burden
Beyond physical health, parasitic infections impose significant psychological and socioeconomic challenges:
- Reduced work productivity
- Educational interruptions
- Increased healthcare expenses
- Potential long-term disability
- Mental health strain from chronic illness
Dangerous Parasites and Their Effects

Opisthorchiidae
Opisthorchis viverrini and Clonorchis sinensis are liver flukes linked to bile duct cancer. These parasites infect the bile ducts, causing inflammation and tissue damage that can lead to cancer over time.
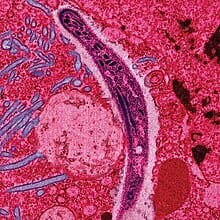
Malaria
Caused by Plasmodium protozoa and transmitted by mosquitoes, malaria is one of the most deadly parasitic infections. It affects millions of people worldwide, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, and can lead to severe symptoms such as fever, chills, and anemia.
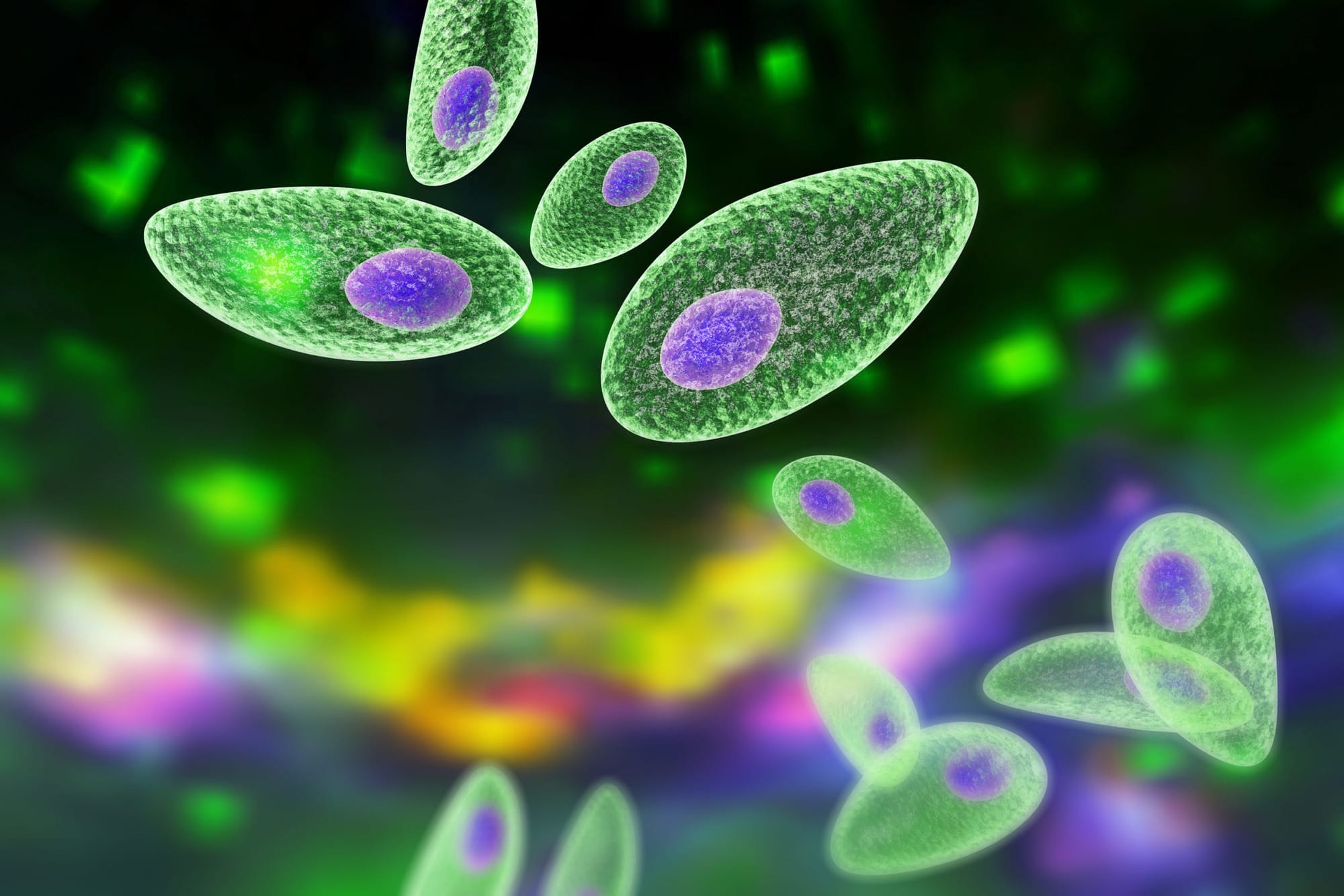
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis, caused by Toxoplasma gondii, can have profound effects on the brain. Studies have suggested a potential connection between toxoplasmosis and psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Chronic Conditions
Chronic parasitic infections can lead to long-term health issues, including chronic fatigue, digestive problems, and nutritional deficiencies. These conditions can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and overall well-being.
Cancer Connection
Certain parasites have been linked to cancer development. For example, Clonorchis sinensis is associated with bile duct cancer, while Schistosoma haematobium is linked to bladder cancer. These connections highlight the importance of early detection and treatment of parasitic infections.
Autoimmune Diseases
There is speculation about potential connections between parasites and autoimmune conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS). Some studies suggest parasitic infections may trigger or exacerbate autoimmune responses, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Digestive Issues
Persistent diarrhoea, abdominal pain, and bloating can indicate the presence of parasites in the gastrointestinal tract.
Weight Loss
Despite adequate nutrition, can be a sign of parasitic infection, as parasites can interfere with nutrient absorption.
Skin Issues
Rashes, itching, and other skin irritations can be symptoms of parasitic infections, particularly ectoparasites like lice and scabies.
Mental Health Symptoms
Anxiety, mood swings, and other mental health symptoms can be linked to parasitic infections, as toxins released by parasites can affect brain function.
Sleep Disturbances
Grinding teeth at night and other sleep disturbances can be signs of parasitic infections, as parasites can disrupt the body's natural rhythms.
Fatigue
Unexplained tiredness and fatigue can be symptoms of parasitic infections, as parasites can drain the body's energy reserves.
Allergies
Increased allergic reactions can be a sign of parasitic infections, as parasites can stimulate the immune system and trigger allergic responses.
Bloating and Gas
Persistent gastrointestinal discomfort, including bloating and gas, can indicate the presence of parasites in the digestive tract.
Weight Gain
Despite dieting, unexplained weight gain can be a sign of parasitic infections, as parasites can interfere with metabolic processes.
Recurring Infections
Frequent illnesses and recurring infections can be a sign of parasitic infections, as parasites can weaken the immune system and make the body more susceptible to other infections.
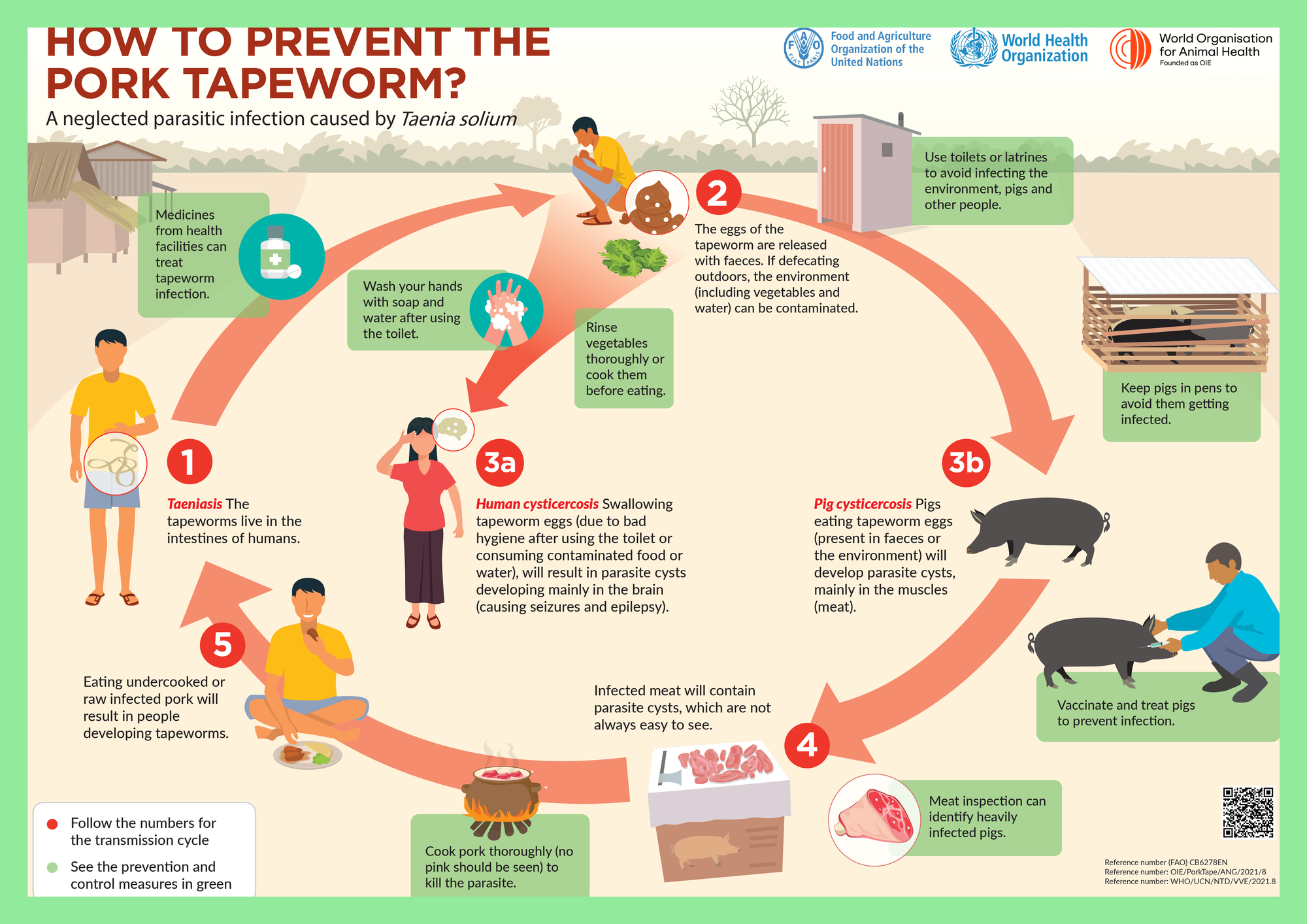
Diagnosis and Detection: Modern Medical Approaches
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Modern medical science has developed sophisticated methods for detecting parasitic infections:
- Comprehensive Stool Analysis
- Blood Tests and Serological Screening
- Advanced Imaging Technologies
- Molecular Diagnostic Techniques
- Genetic and PCR Testing
PREVENTION STRATEGIES: Protecting Yourself and Your Community
Comprehensive parasite prevention requires a multifaceted approach:
Personal Hygiene
- Regular handwashing
- Proper food preparation techniques
- Using clean water sources
- Wearing protective footwear
Environmental Management
- Improved sanitation infrastructure
- Water treatment systems
- Waste management
- Vector control program
Medical Interventions
- Regular health screenings
- Timely medical treatments
- Vaccination where applicable
- Community health education

Treatment Options: Modern Medical Interventions
- Antiparasitic Medications
- Broad-spectrum treatments
- Targeted drug therapies
- Combination treatment protocols
- Supportive Care
- Nutritional support
- Immune system strengthening
- Symptom management
Emerging Research: The Future of Parasite Management
Cutting-Edge Scientific Developments
Ongoing research promises more effective prevention and treatment:
- CRISPR gene-editing technologies
- Advanced diagnostic algorithms
- Innovative vaccine development
- Precision medicine approaches
Conclusion: A Call for Awareness and Action
Parasitic infections represent a complex global health challenge that demands continuous attention, research, and proactive management. Individuals can significantly reduce their risk by understanding transmission routes, potential health impacts, and prevention strategies and contribute to broader public health initiatives.