Mind-Mouth Connection: Your Oral Bacteria Could Be Shaping Your Brain's Future
Emerging research suggests that the complex ecosystem of microorganisms in our mouth - known as the oral microbiome - may play a crucial role in cognitive health and could potentially influence the development of cognitive decline.

Could the secret to maintaining cognitive health be hiding in your mouth? Recent scientific discoveries have revealed an intriguing connection between the microscopic community living in our oral cavity and our brain function. This emerging research suggests that the complex ecosystem of microorganisms in our mouth—known as the oral microbiome—may play a crucial role in cognitive health and could potentially influence the development of cognitive decline. With an estimated 50 million people worldwide living with dementia and numbers projected to triple by 2050, understanding this connection has never been more critical.
The Hidden Universe in Your Mouth: Decoding the Oral Microbiome
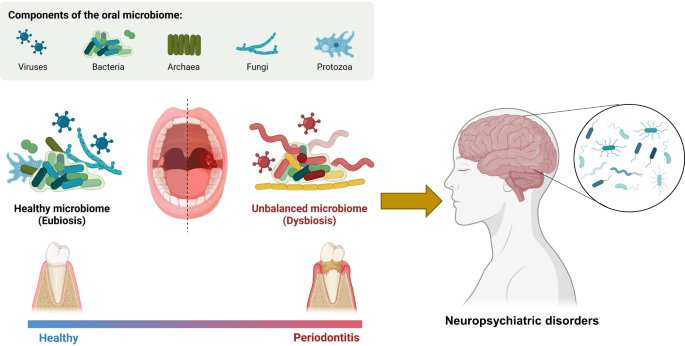
The oral microbiome is a diverse community of microorganisms that live in our mouths. This intricate ecosystem comprises hundreds of species of bacteria, fungi, and other organisms, with current estimates suggesting approximately 700 different species coexist in this environment. To put this diversity into perspective, there are around 20 billion bacterial cells in your mouth, which exceeds Earth's human population by more than twice.
A balanced oral microbiome is essential for maintaining not just oral health, but also systemic wellness. These microorganisms participate in various biological processes, from helping break down nutrients to protecting against harmful pathogens. Research shows that a single millilitre of saliva can contain up to 100 million bacterial cells, and these tiny organisms contribute significantly to our health through various mechanisms, including:
- Production of vitamins B12, K2, and other essential nutrients
- Protection against harmful pathogens through competitive exclusion
- Regulation of pH levels in the mouth
- Support of immune system development and function
The Brain-Bacteria Blueprint: Unveiling the Oral-Cognitive Connection
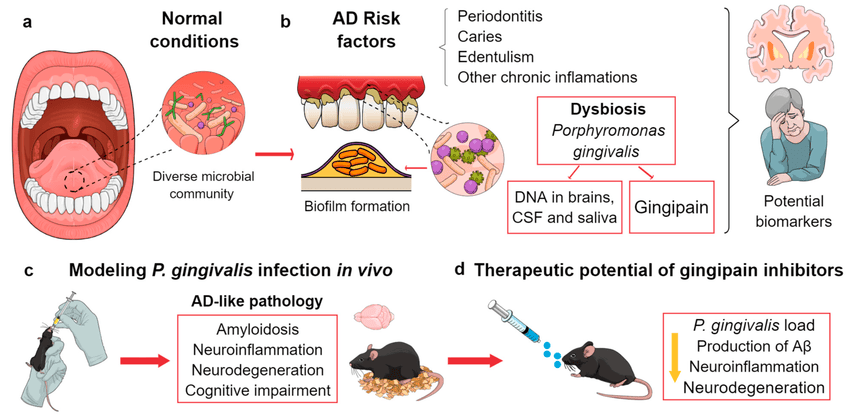
Recent research has uncovered fascinating connections between oral microbiome composition and cognitive health. Studies have particularly highlighted the role of bacteria from the genus Neisseria, which has been associated with improved cognitive functions, including enhanced working memory and executive function. A groundbreaking study published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease found that individuals with poor oral health were 23% more likely to experience cognitive decline.
The relationship between oral health and cognitive function operates through several potential mechanisms:

First, pathogenic bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream, potentially reaching the brain and influencing neural function. Research has shown that P. gingivalis, a common oral pathogen, has been found in the brains of Alzheimer's patients at rates significantly higher than in age-matched controls.
Second, beneficial oral bacteria play a crucial role in producing nitric oxide, a compound supporting synaptic plasticity—the brain's ability to form and reorganize neural connections. Studies indicate that proper nitric oxide levels can improve memory performance by up to 20% in older adults.
The Food-Microbiome Matrix: Dietary Keys to Cognitive Enhancement
Diet plays a fundamental role in shaping our oral microbiome. The Mediterranean diet, rich in nitrates from vegetables like leafy greens and beets, has been shown to promote the growth of beneficial bacteria that support cognitive function. Research indicates that individuals following a Mediterranean diet have up to 40% lower risks of cognitive decline than those following a Western diet.

Some key dietary components that support oral microbiome health include:
- Nitrate-rich foods (beetroot, spinach, arugula) - containing 250+ mg nitrates per 100g
- Polyphenol-rich foods (berries, green tea, dark chocolate) - shown to reduce harmful bacteria by up to 40%
- Fibre-rich foods that act as prebiotics, supporting beneficial bacterial growth
- Fermented foods containing natural probiotics

Prebiotics and probiotics represent another promising avenue for maintaining a healthy oral microbiome. Clinical trials have shown that specific oral probiotic strains can reduce the presence of harmful bacteria by up to 60% while promoting the growth of beneficial species.
The Silver Tsunami: Ageing Population and Cognitive Health Crisis
Understanding the connection between oral health and cognitive function becomes increasingly crucial as our global population ages.
Current statistics paint a concerning picture:
- 15-20% of adults aged 65 and older have mild cognitive impairment (MCI) - 32% of people with MCI develop Alzheimer's disease within 5 years - Poor oral health is associated with a 28% increased risk of developing dementia
To maintain a healthy oral microbiome and potentially support cognitive health, consider implementing these evidence-based strategies:
- Schedule regular dental check-ups (recommended every 6 months)
- Incorporate nitrate-rich foods into daily meals (aim for 300-400mg nitrates daily)
- Use specialized oral probiotics with clinically proven strains
- Maintain consistent oral hygiene practices, including proper brushing technique and regular flossing
Frontiers of Discovery: What's Next in Oral-Brain Research
While current research has revealed fascinating connections between oral health and cognitive function, many questions remain unanswered. Future studies need to explore:
- The long-term effects of dietary modifications on both oral microbiome composition and cognitive outcomes
- Detailed mechanistic investigations into how specific bacterial species influence brain health
- The potential development of targeted interventions to support beneficial oral bacteria
- The role of the oral microbiome in preventing age-related cognitive decline
Research funding in this area has increased by 150% in the past decade, reflecting growing recognition of its importance in public health.
Beyond the Brush: A New Paradigm for Brain Health
The connection between oral health and cognitive function represents an exciting frontier in our understanding of brain health. By maintaining a healthy oral microbiome through good dental care, dietary choices, and targeted probiotic interventions, we may be able to support cognitive health throughout our lives.
The journey to better brain health might start with paying more attention to the billions of tiny allies in your mouth. The future of cognitive health could be as close as your next smile.