Cellular Elixir: NAD's Promising Role in the Fight Against Aging
The link between NAD and aging has been a subject of intense research. Scientists have discovered that maintaining healthy NAD levels may be crucial in combating the effects of aging.

In the quest for eternal youth, scientists have long sought to unravel the mysteries of aging. One molecule that has captured significant attention in recent years is NAD, or Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide. This unassuming compound in every cell of our bodies may hold the key to understanding – and potentially slowing – the aging process. Let's examine the fascinating world of NAD and explore its crucial role in our cellular health and longevity.
Understanding NAD: The Cellular Powerhouse
NAD is a coenzyme found in all living cells. It is pivotal in numerous metabolic processes, critical for energy production and cellular repair. Think of NAD as the cellular equivalent of a rechargeable battery – it exists in NAD+ (the oxidized form) and NADH (the reduced form).
The importance of NAD in our bodies cannot be overstated. It is involved in hundreds of metabolic processes, including:
- Energy production in mitochondria
- DNA repair
- Gene expression regulation
- Cellular signalling
- Maintaining cellular health and function
As we age, our NAD levels naturally decline. This decrease is associated with various age-related issues, including decreased energy metabolism, reduced cellular repair, and increased susceptibility to age-related diseases.
The NAD-Aging Connection: Unlocking the Secrets of Longevity
The link between NAD and aging has been a subject of intense research in recent years. Scientists have discovered that maintaining healthy NAD levels may be crucial in combating the effects of aging. Here's how NAD fights against the aging process:
1. Cellular Repair and Energy Production
NAD is essential for the optimal functioning of mitochondria, our cells' powerhouses. As NAD levels decline with age, so does our cells' ability to produce energy efficiently. This can lead to a cascade of age-related issues, from decreased physical stamina to cognitive decline.
Moreover, NAD is crucial in activating enzymes involved in DNA repair. As we age, our DNA accumulates damage from various sources (e.g. UV radiation, oxidative stress). NAD-dependent enzymes help repair this damage, maintaining the integrity of our genetic material.

2. Sirtuin Activation: The Longevity Connection
One of the most exciting discoveries in aging research has been the role of sirtuins – a family of proteins that regulate various cellular processes related to aging and longevity. NAD is a critical activator of sirtuins, particularly SIRT1 and SIRT3.
When activated by NAD, sirtuins can:
- Improve mitochondrial function
- Enhance cellular stress resistance
- Regulate circadian rhythms
- Influence metabolism and energy balance
These effects collectively contribute to improved cellular health and potential lifespan extension.
3. Research Findings: NAD Levels and Aging
Numerous studies have demonstrated the correlation between NAD levels and aging:
- In animal studies, boosting NAD levels has been shown to extend lifespan and improve various health markers.
- Human studies have found that NAD levels decline significantly with age, potentially contributing to cellular dysfunction.
- Restoring NAD levels in older animals has improved muscle function, cardiovascular health, and cognitive performance.
While more research is needed, especially in human subjects, the current evidence suggests that maintaining healthy NAD levels could be a promising strategy for promoting healthy aging.
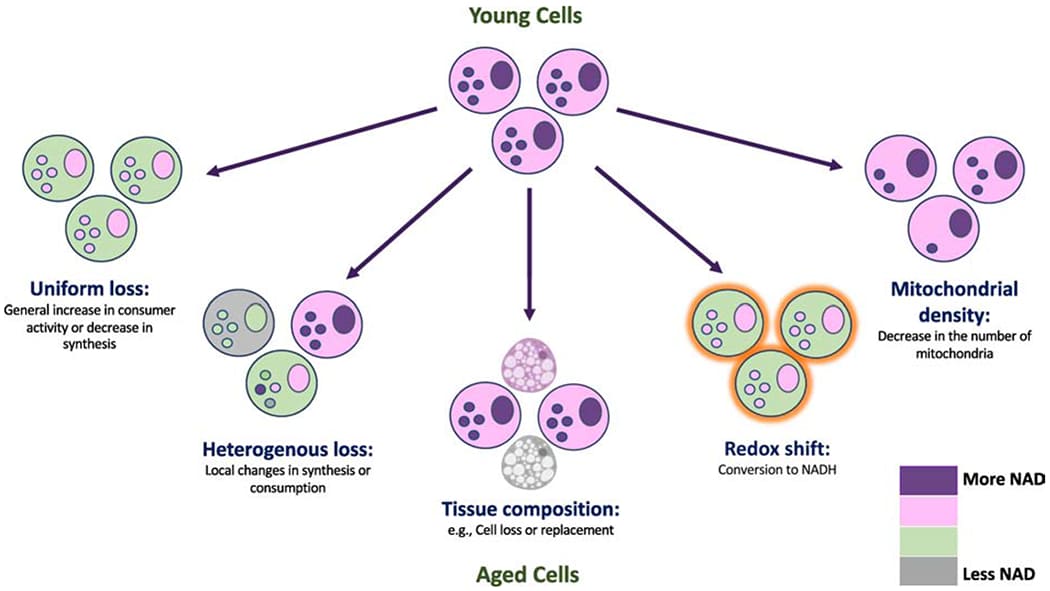
What Causes Decreases in NAD+?
Aging isn't the only physiological phenomenon known to reduce our body's production of NAD+. There are several other factors, including:
- DNA damage.
- Alcohol use.
- Overeating.
- High blood sugar and insulin levels. An excessive rise in blood sugar levels or reduction in insulin levels affects the NADH-NAD+ ratio and lowers the NAD+ levels.
Boosting NAD Naturally: Diet and Nutrition
The good news is that we can influence our NAD levels through improved dietary and lifestyle choices. Let's explore some natural ways to boost NAD production in our bodies.
NAD Precursors: The Building Blocks
Our bodies can synthesize NAD from several precursor molecules, including:
- Niacin (Vitamin B3)
- Nicotinamide
- Nicotinamide Riboside (NR)
- Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)
- Tryptophan (an essential amino acid)
Consuming foods rich in these precursors can help support healthy NAD levels.
NAD-Boosting Foods
Incorporating the following foods into your diet can help maintain healthy NAD levels:
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of niacin and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients support NAD production and other health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health and cognitive function.
- Dairy: Milk, particularly cow's milk, contains nicotinamide riboside, a direct precursor to NAD. While more research is needed to determine the bioavailability of NR from dairy sources, including milk in your diet may support overall metabolic health.
- Green Vegetables: Leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables like asparagus, broccoli, and peas are rich in vitamins and minerals that support NAD synthesis. They're also packed with antioxidants that can help protect cells from damage.
- Mushrooms: Certain mushroom varieties, particularly crimini mushrooms, are excellent sources of niacin. They also contain other beneficial compounds that support overall health and potentially contribute to longevity.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, wheat bran, and other whole grains are rich in B vitamins, including niacin, for NAD production. They also provide fibre and other nutrients that support overall health.
- Nuts and Seeds: Peanuts, sunflower seeds, and avocados are good sources of niacin and other B vitamins that support NAD synthesis.
- Fermented Foods: Kombucha, kimchi, plain yoghurt, sauerkraut, etc.

Lifestyle Factors That Influence NAD Levels
In addition to diet, several lifestyle factors can impact your NAD levels:
- Caloric Restriction: Studies have shown that moderate caloric restriction can increase NAD levels and activate sirtuins, potentially promoting longevity. However, it's crucial to maintain proper nutrition while reducing calorie intake.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, particularly high-intensity exercise, can boost NAD levels by creating a form of energy stress that stimulates NAD production.
- Intermittent Fasting: Intermittent fasting has been shown to increase NAD levels and activate sirtuins.
- Sun Exposure: While excessive exposure is harmful, moderate sun exposure can help boost NAD levels. However, always practice safe sun habits to protect your skin.
- Sauna Use: Some studies suggest that heat stress, such as that experienced in a sauna, may increase NAD levels. However, more research is needed in this area.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can deplete NAD levels. Stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga may help maintain healthy NAD levels.

The Supplement Question: NAD Boosters
As interest in NAD's potential anti-aging effects has grown, so has the market for NAD-boosting supplements. The most popular options include:
- Nicotinamide Riboside (NR): A form of vitamin B3 that's a direct precursor to NAD.
- Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN): Another direct precursor to NAD.
- Niacin and Niacinamide: Forms of vitamin B3 that can be converted to NAD in the body.
While these supplements have shown promise in animal studies and small human trials, more research is needed to understand their long-term effects and optimal dosing. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Embracing NAD for Healthy Aging
As we've explored, NAD plays a crucial role in cellular health and may be a key factor in slowing the aging process.
- Eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Manage stress effectively
- Get adequate sleep
- Stay socially connected and mentally engaged

By combining these strategies with NAD-supporting habits, you can take proactive steps towards aging gracefully and maintaining vitality throughout your life.
The goal isn't just to add years to your life, but life to your years. By nurturing your NAD levels, you're investing in your cellular health, potentially paving the way for a more vibrant, energetic, and fulfilling journey through the later stages of life.






