Health Benefits of Sprouting Seeds: Small But Powerful
From boosting nutrient bioavailability to aiding digestion and blood sugar regulation, sprouted seeds are a simple yet profound addition to any diet.

Have you ever wondered why sprouted seeds are gaining immense popularity among health enthusiasts? These tiny, nutrient-dense powerhouses offer benefits that significantly enhance your overall well-being. From boosting nutrient bioavailability to aiding digestion and blood sugar regulation, sprouted seeds are a simple yet profound addition to any diet. In this article, we'll delve into the remarkable advantages of sprouting seeds, and explore how you can effortlessly incorporate them into your daily routine.
What Are Sprouts?
Definition and types of sprouts
Sprouts are the young, edible shoots that emerge from germinated seeds, grains, or legumes. They are typically harvested within a few days after the sprouting process begins, ensuring their tender, nutrient-rich state. Seeds that can be sprouted include broccoli, radish, chickpeas, mung beans, lentils and many others.
Why is the content of sprouted seeds so enhanced?
The sprouting process initiates a remarkable transformation within the seed, unlocking its full nutritional potential. As the seed germinates, it breaks down complex molecules, such as starches and proteins, into simpler forms that are easier for the body to absorb and utilize. This process also increases the bioavailability of essential vitamins, minerals, and beneficial plant compounds.

Nutrient level comparison - sprouted vs. "unsprouted" seeds
Studies have shown that sprouted seeds can contain significantly higher levels of nutrients compared to their unsprouted (ungerminated) counterparts. For instance, sprouted grains and legumes can boast up to three times the amount of vitamin C, five times the vitamin B, and eight times the vitamin E content found in their unsprouted forms.
Sprouts May Help Control Blood Sugar Levels
Emerging research suggests that incorporating sprouted seeds into your diet may help maintain healthy blood sugar levels. A study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that individuals who consumed a diet rich in sprouted grains and legumes experienced improved insulin sensitivity and better blood sugar control.
The potential blood sugar-regulating properties of sprouts can be attributed to their high fibre content, which slows down the absorption of carbohydrates and prevents rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. The antioxidants and beneficial plant compounds in sprouts may also enhance insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Consuming Sprouts May Improve Digestion
Sprouts are a rich source of dietary fibre, essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Fibre promotes regular bowel movements, prevents constipation and supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, contributing to overall digestive well-being.
Apart from fibre, sprouts are also abundant in enzymes that break down complex nutrients, making them easier to digest. These enzymes include amylases, which help break down starches; and proteases that assist in protein digestion. This natural enzyme content in sprouts can alleviate digestive discomfort and support optimal nutrient absorption.
Sprouts May Improve Heart Health
Sprouts are emerging as potential allies in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. Their unique nutritional profile, rich in fibre, antioxidants, and beneficial plant compounds, may contribute to lowering the risk of heart disease.
The high fibre content in sprouts can help lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, sprouts are a good source of folate, a vitamin essential for maintaining healthy homocysteine levels linked to a lower risk of heart disease. Furthermore, the antioxidants present in sprouts may help prevent oxidative stress and inflammation, two key factors in the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Raw Sprouts May Contain Harmful Bacteria
While sprouts offer numerous health benefits, be aware of the potential risks of consuming raw sprouts, particularly if you are not sprouting the seeds yourself. Raw sprouts have been linked to several foodborne illness outbreaks caused by harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella and E. coli.
To minimize the risk of bacterial contamination, it is recommended to follow proper food safety practices when handling and consuming sprouts. This includes thoroughly washing sprouts before consumption, avoiding cross-contamination with other foods, and cooking sprouts to eliminate harmful bacteria.
How to Include Sprouts in Your Diet
Sprouts are incredibly versatile and can be easily incorporated into many dishes. They can be added to salads, sandwiches, stir-fries, and smoothies. Sprouted grains and legumes can also be used in soups, stews, and baked goods, adding a nutritional boost to your meals.
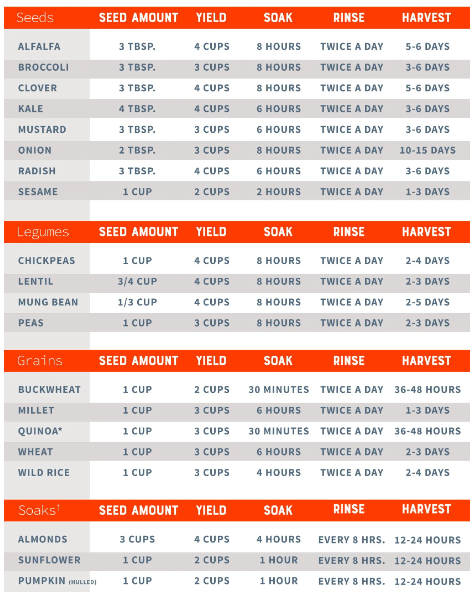
What are some tips for successful sprouting at home?
For successful sprouting at home, ensure that you use high-quality seeds specifically intended for sprouting. Follow proper sanitation practices, rinse the sprouts regularly, and provide adequate air circulation and drainage. Additionally, monitor the sprouts closely and discard any that appear discoloured or have an odour.




From Seeds to Sprouts: DIY Guide
How do you sprout seeds?
A large variety of seed "sprouters" are available in Health Shops and Pharmacies, from jars, stainless steel and Plastic options. Choose one that appeals to you and start sprouting.
The following video provides a detailed guide to start sprouting using mason jars.
Recipes and meal ideas featuring sprouted seeds
Here are a few delicious and nutritious recipe ideas featuring sprouted seeds:
- Sprouted Lentil and Quinoa Salad: Toss together sprouted lentils, quinoa, vegetables, and a tangy vinaigrette for a protein-packed meal.
- Avocado Toast with Sprouted Mung Beans: Top your avocado toast with crunchy mung beans for added texture and nutrition.
- Sprouted Grain Bread: Substitute a portion of the regular flour with sprouted grains for a nutrient-dense and flavorful loaf of bread.
- Sprouted Chickpea Hummus: Blend chickpeas with tahini, lemon juice, and garlic for a creamy and nutritious dip or spread.
Sprouted seeds are a true superfood that should be a staple in any health-conscious individual's diet. From boosting nutrient bioavailability to aiding in digestion and blood sugar regulation, these tiny powerhouses offer a myriad of benefits. Incorporate sprouted seeds into your meals, experiment with different varieties, and embrace the incredible nutritional value they bring to your plate. Embrace the power of sprouting and nourish your body with these nutrient-dense wonders.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are sprouted seeds good for health?
Yes, sprouted seeds are incredibly beneficial for overall health. They are packed with essential nutrients, antioxidants, and beneficial plant compounds that can support various bodily functions, including digestion, blood sugar regulation, and cardiovascular health.
What is the healthiest seed to sprout?
Some of the healthiest seeds to sprout include broccoli, alfalfa, radish, mung bean, and lentil seeds. These sprouts are rich in vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants, making them excellent additions to a nutritious diet.
What happens when you eat sprouts every day?
Incorporating sprouts into your daily diet can provide many health benefits. Regular consumption of sprouts may help improve digestion, regulate blood sugar levels, support heart health, and provide you with essential nutrients and antioxidants for optimal health.
Are there any side effects from consuming sprouted seeds?
When consumed in moderation, sprouted seeds are generally safe and well-tolerated. However, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort, such as bloating or gas, due to the high fibre content in sprouts. Additionally, it is crucial to properly handle and cook sprouts to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses from potential bacterial contamination.
Can sprouted seeds be consumed raw?
While sprouts can be consumed raw, it is generally recommended to cook them thoroughly to eliminate the risk of potential bacterial contamination, such as Salmonella or E. coli. Proper food handling and preparation practices should be followed when consuming raw sprouts.
How long do sprouted seeds last?
Sprouted seeds have a relatively short shelf life and should be consumed within a few days of sprouting for optimal freshness and nutrient retention. It is best to store them in the refrigerator.
Can sprouted seeds be frozen?
Yes, sprouted seeds can be frozen to extend their shelf life. However, the process may affect their texture and nutrient content. If you plan to freeze sprouts, it is best to blanch them first to preserve their quality.
Are sprouted seeds suitable for people with food allergies?
Individuals with food allergies or sensitivities should exercise caution when consuming sprouted seeds, as the sprouting process may alter the allergenic properties of the seeds. If you have known food allergies, consult a healthcare professional before incorporating sprouted seeds into your diet.






